IUD insertion and removal in Warsaw
We offer a range of services for the selection of reliable contraception in Warsaw: from consultation to insertion and/or removal of the IUD.
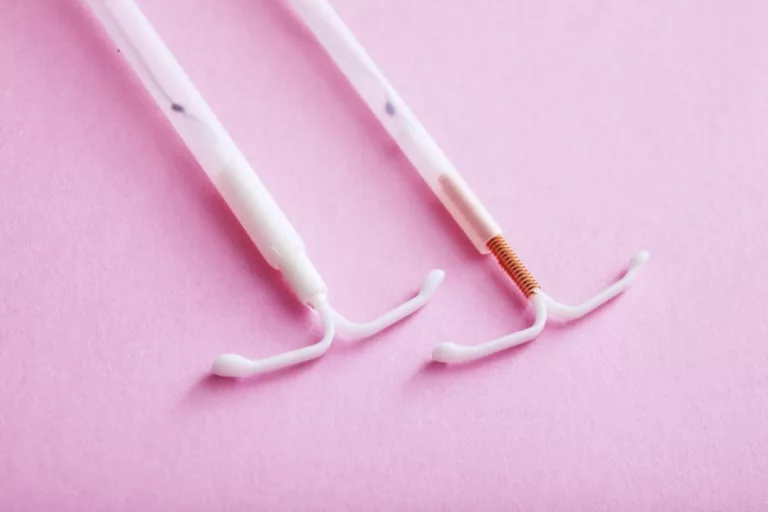
An intrauterine device (IUD) is a tiny device, most often T-shaped, that is inserted in the uterine cavity to prevent pregnancy (and not only – more on that below).
It is long-term, reversible and one of the most effective methods of contraception.
There are 5 different brands of IUDs approved by the FDA. They are divided into 2 types:
- Non-hormonal copper IUD (Paragard)
- does not block ovulation;
- prevents the “meeting” of the sperm with the egg – prevents fertilization;
- if the first mechanism did not work, and fertilization still occurred, the second one turns on – the obstacle to the implantation of the embryo in the uterine cavity – due to the influence of a foreign body;
- it is the most effective method of emergency contraception when it is inserted into the uterine cavity within 120 hours (5 days) after unprotected sexual intercourse
- it is inserted for up to 10 years;
- protects against pregnancy by ~99.4% (WHO).
- Hormonal IUD (Mirena, Kyleena, Liletta, Skyla)
- contains the hormone levonorgestrol (progestin);
- unlike a copper IUD, it can block ovulation;
- thickens mucus in the cervix, thereby making it difficult for spermatozoa to enter the uterine cavity;
- in case of fertilization (which is extremely rare), as well as the copper IUD, due to its influence as a foreign body – it prevents the implantation of the embryo in the uterine cavity;
- inserted for up to 8 years depending on the type of IUD (Mirena and Liletta can stay in the uterine cavity for up to 8 years, Kyleena – up to 5 years, Skyla – up to 3 years).
- protects against pregnancy by ~99.8% (WHO).
The IUD is inserted after initial examination and taking swabs, on any day of the menstrual cycle, if we are absolutely sure that there is no pregnancy. Its contraceptive effect, when used with a copper IUD, “turns on” immediately, and with the hormonal one – 7 days after insertion (if it was inserted later than 7 days after the first day of menstruation).
The IUD insertion is usually painless and lasts about 5 minutes.
IUD advantages:
- it is a safe, economical (you pay once and forget for a couple of years) and one of the most effective methods of pregnancy prevention;
- easy to use – you have an IUD inserted in 5 minutes and now you are protected from pregnancy 24/7 for the next 3-10 years, depending on the type of IUD;
- does not require the participation of the partner (they may not know about the existence of the IUD at all, you decide);
- there is no evidence that IUDs will affect your weight or increase your risk of cervical/uterine/ovarian/breast cancer;
- can be used during breastfeeding;
- The IUD can be removed at any time, and it does NOT affect your fertility – you can get pregnant in the first cycle after its removal;
- does not carry the risk of side effects associated with contraceptive methods containing estrogen.
Hormonal IUDs make periods more scanty after 3 months of use, and in ~20% of users they may disappear a year after IUD placement. This is expected and NORMAL. There is no reason to worry – your cycle will be back just after the IUD is removed.
Due to its non-contraceptive advantages, hormonal IUDs can be prescribed in the following cases:
- to reduce menstrual pain (treatment of dysmenorrhea);
- to reduce pain caused by endometriosis;
- to reduce the risk of endometrial cancer (especially for women with endometrial hyperplasia);
- to treat heavy menstruation;
- to treat endometrial hyperplasia (Mirena is a first-line therapy in this case);
- to treat adenomyosis;
- to treat uterine fibroids.
IUD disadvantages:
- IUDs do not protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs), so if you are not sure about your partner, you should additionally use a condom;
- IUDs containing copper can lead to more abundant and prolonged menstruation. Usually, after a few months, everything returns to normal;
- if you have an IUD inserted in the presence of some infectious process (gonorrhea, chlamydia), it can cause inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs. Therefore, it is recommended to be tested for STDs before placing an IUD;
- most women who stop using an IUD do so because of vaginal bleeding or severe pain, although these side effects are rare.
Risks associated with IUD placement:
- falling out of the IUD. It happens rarely;
- yeast infection. There is very limited evidence that women with IUDs are more likely to develop thrush and bacterial vaginosis. If you have an IUD inserted and at the same time you suffer from recurrent thrush, this may be a reason to switch to another method of contraception;
- PID (pelvic inflammatory disease). Again, this is usually a case where you were under-screened before the IUD was placed;
- uterine perforation. You have to “try hard” to make it happen, although there are different situations. In any case, this happens extremely rarely;
- lower abdomen pain for several days after the IUD insertion;
- intermenstrual bleeding – usually goes away 3-5 months after IUD insertion.
You should immediately seek medical help if:
- it seems to you that the IUD has shifted or fallen out;
- there is a possibility that you are pregnant;
- you have fever;
- severe pain in the lower abdomen, which does not go away;
- if profuse bleeding from the genital tract has developed.
Contraindications to the hormonal IUD insertion:
- pregnancy/suspected pregnancy;
- pathology of the uterus, leading to deformation of the uterine cavity.
- sexually transmitted diseases;
- active inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs;
- known or suspected oncology of the uterus and cervix;
- vaginal bleeding of unknown etiology;
- acute cervicitis, vaginitis or other infections of the lower parts of the genital tract;
- severe liver dysfunction;
- known or suspected malignant breast tumors;
- known allergic reaction to progestins.
Contraindications to the copper IUD insertion:
- pregnancy/suspected pregnancy;
- pathology of the uterus, leading to deformation of the uterine cavity;
- sexually transmitted diseases, active inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs.
- active inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs;
- known or suspected oncology of the uterus and cervix;
- vaginal bleeding of unknown etiology;
- acute cervicitis, vaginitis or other infections of the lower parts of the genital tract;
- Wilson’s disease;
- hypersensitivity to any IUD component, including copper.
Who can use the IUD?
- Teenagers;
- Women who have not given birth;
- Women after childbirth;
- Nursing mothers.
The intrauterine device (IUD) can be inserted as soon as a few minutes after childbirth.
The optimal time for the procedure: An IUD can be inserted on any day of the menstrual cycle, but optimally – towards the end of menstruation.
Before inserting the IUD, you need to undergo:
- Pregnancy test
- Gynecological examination.
- Tests for sexually transmitted infections.
After the IUD is inserted, you may be recommended to regularly check for the presence of “strings” (threads) of the IUD.
Recommendations after IUD insertion:
- For the next 10 days, avoid lifting heavy weights and engaging in intense workouts.
- It is not recommended to take hot baths or visit saunas for 7-10 days.
- You can take anti-inflammatory medication within the first week if you experience pain.
- You can resume sexual intercourse after a few days following the procedure.
- Visit your doctor for a follow-up appointment after 7 days, and then again after a month.
IUD Removal
Removing an IUD is a simpler and quicker process compared to its insertion. It’s best to do this on the day of menstruation.